Using Electronic Resources Management (ERM)
Electronic Resource Management (ERM) allows you to manage the relationship between your library and providers of electronic metadata and text, such as abstract, index, and full-text databases, including databases of serials in electronic format. These databases are called resources.
Use of resources such as abstract, index, and full-text databases is typically licensed to a library for a period of time.
Electronic serials (sometimes referred to as electronic titles), like print serials, can be purchased through subscriptions. Electronic serials have coverage data, which is similar in concept to holdings data. (Print serials and print serials vendors are managed with Serials.)
The process of setting up a new resource is:
- Create a resource record.
- Create a license record.
- Load coverage data.
ERM allows you to manage resource providers by using the following record types and table:
| Data is stored in: | Purpose of data: |
|---|---|
| resource records |
|
| license records | resource licensing details |
| coverage table | electronic serial subscription data |
| contact records | how to contact the resource provider |
| order records | paying for the resource |
The following diagram shows the relationship of these records and table in your system:
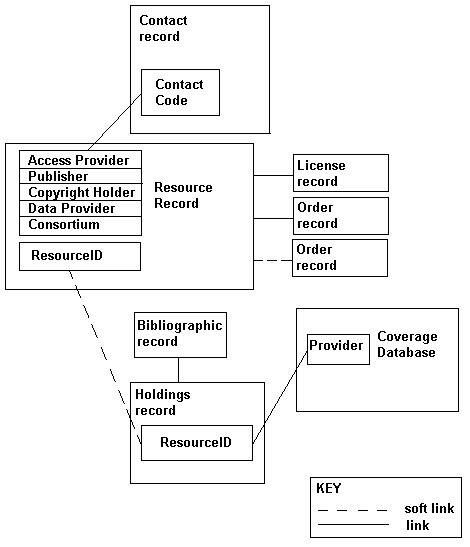
With ERM, you can:
- manage resource providers
- track negotiations about resources
- manage licensing of resources
- manage contacts for resources
- manage incidents for resources
- manage renewals
- track costs associated with resources
- restrict access to resources
- map a resource to another resource name
- store information about electronic titles held within resources
- display coverage data for titles
- use ERM with Acquisitions to manage payments for resources
- display links in the WebPAC to resources and electronic titles held within resources
Resource Record Link Limitations
In Create Lists, you cannot export resource record fields from a list of order records. When a resource is linked directly to an order, you also cannot print or send purchase orders with the resource name instead of the title.