INN-Reach Admin Status and Configuration Options
Links under the General heading on the INN-Reach Admin tool home page (or on the Status menu) offer options for viewing status and statistics, configuration and mappings, and data synchronization.
See:
- Viewing Status and Statistics
- Viewing Your System Configuration and Mappings
- Data Upload and Synchronization
Viewing Status and Statistics
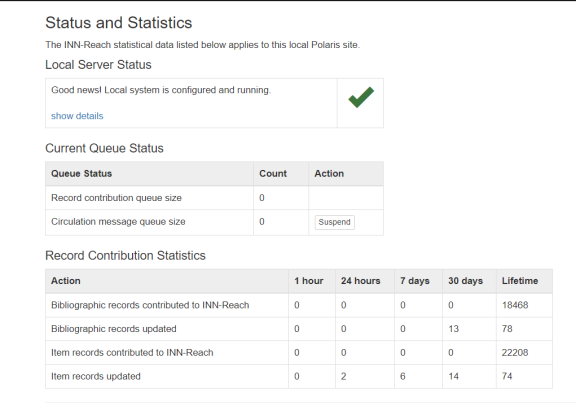
Click Status and Statistics under the General heading for the following functions:
- View information about your local Polaris server status.
- View current queue status information and suspend/resume outgoing circulation API messages.
- Suspending or resuming circulation API messages requires the INN-Reach Modify user permission. Otherwise, the Action column and the buttons do not appear.
- When you select the Suspend button, the Resume button appears.
- View record contribution statistics for your local Polaris server.
Viewing Your System Configuration and Mappings
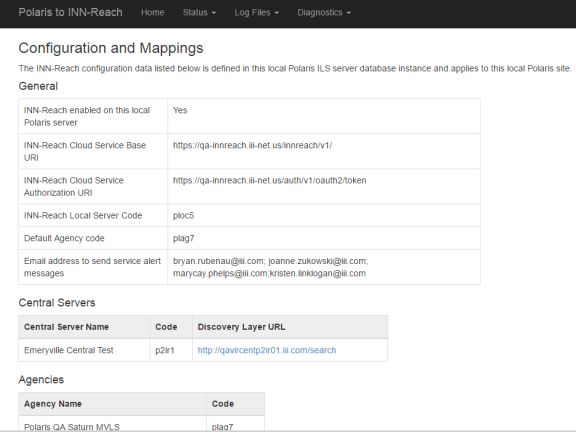
Click Configuration and Mappings under the General heading to view the following information:
- General URIs, local server/agency code, and email addresses for service alerts
- Central server URL
- Agencies participating in this INN-Reach consortium
- Filters
- Polaris branches participating in this INN-Reach consortium
- Item status mappings
- Material type mappings
- Collection mappings
- Central IType (item type) to Polaris format mappings
- Polaris Patron Code to INN-Reach local PType (patron type) mappings
- INN-Reach Central PType to Polaris Patron Code mappings
The mappings are created with the help of Innovative support when your library joins a central INN-Reach consortium. See INN-Reach Configuration and Mapping Profile for more information. Contact Innovative support if you need to change email alert addresses or Polaris/central mappings.
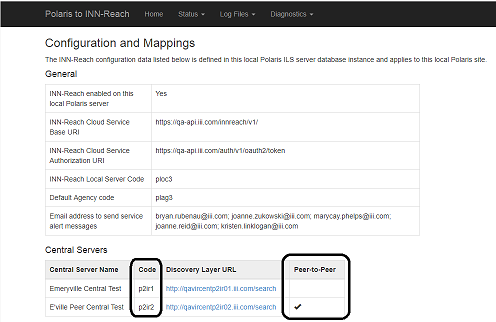
If your library participates in INN-Reach Peer-to-Peer Circulation (see INN-Reach Peer-to-Peer Circulation) and more than one Central has been defined in the InnReachCentrals table, a Peer-to-Peer display column indicates the peer-to-peer Central(s). In the example below, p2ir1 indicates the Central to which the library contributes records and circulates materials; p2ir2 with the check mark indicates the peer-to-peer Central that can circulate materials to p2ir1 patrons; however, the library does not contribute records to p2ir2.
Data Upload and Synchronization
Click Data Upload and Synchronization under the General heading if your upload configuration has changed and you need to synchronize your local data with INN-Reach central data.
Note:
You need the INN-Reach administration: Modify permission to access Data Upload and Synchronization.
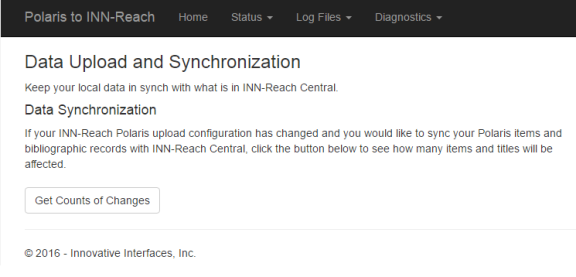
Click get Counts of Changes to see how many records will be affected. If any will be affected by synchronization, the tool displays a Populate Queue option. Click Populate Queue to synchronize the local and central data.
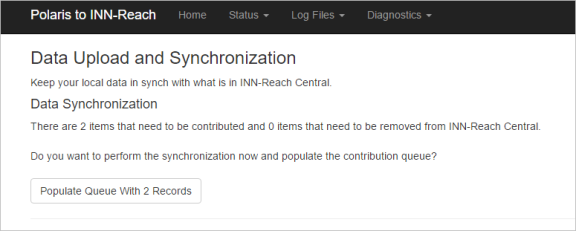
Once local and central data are synchronized, any records needing uploading or removing would be due to errors. Typically, bibs and items added to the catalog or modified are handled through normal sync processing, and no manual synchronization is necessary.